Adding an Individual Property¶
Properties of individual identifier can be added, removed and edited in the KB Editor. Click to select an individual identifier in the KB Editor taxonomy window, relevant tables for the individual will show up in the KB Editor editing window. The 2 buttons to the left of the Types table can be used to add a new type and edit all types of the selected individual. Similarly, the 2 buttons to the left of the Individual Properties table can be used to add a new property and edit all properties of the individual. Next to each existing property in the Individual Properties table are also 2 buttons, one for deleting and the other for editing the property. Some properties may allow multiple values. When the number of values for such a property is below its maximum cardinality, there will be new entry in the Individual Properties table to add a new value to the property. The example in Fig. 171 shows the Types and Individual Properties tables belonging to selected individual Benjamin and the edit buttons available for these tables.
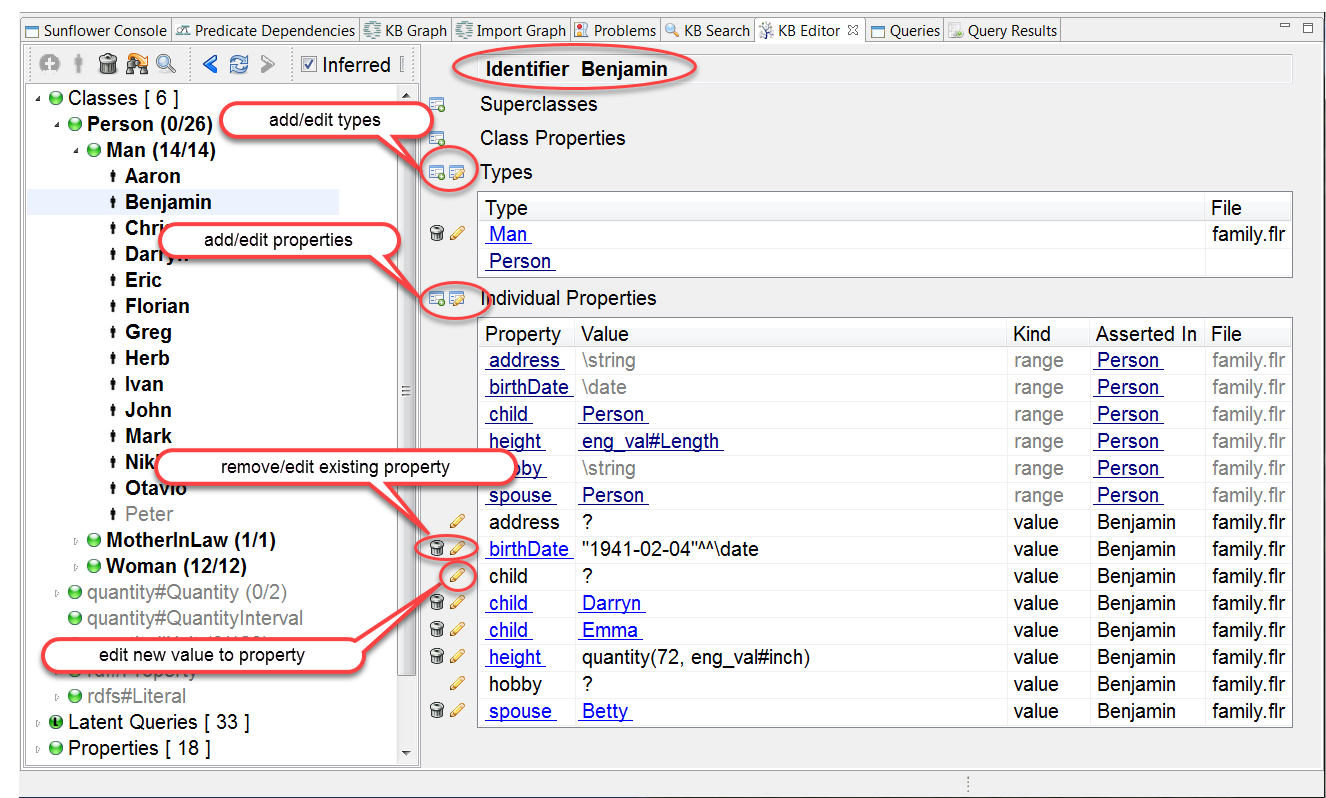
Fig. 171 Editing buttons in KB Editor editing window
Click the Add an individual property to the individual button, the button changes into a green check mark, and a new row is added to the property table with editing enabled for all applicable fields, as shown in Fig. 172. When the green check mark is clicked again, the new row is saved.
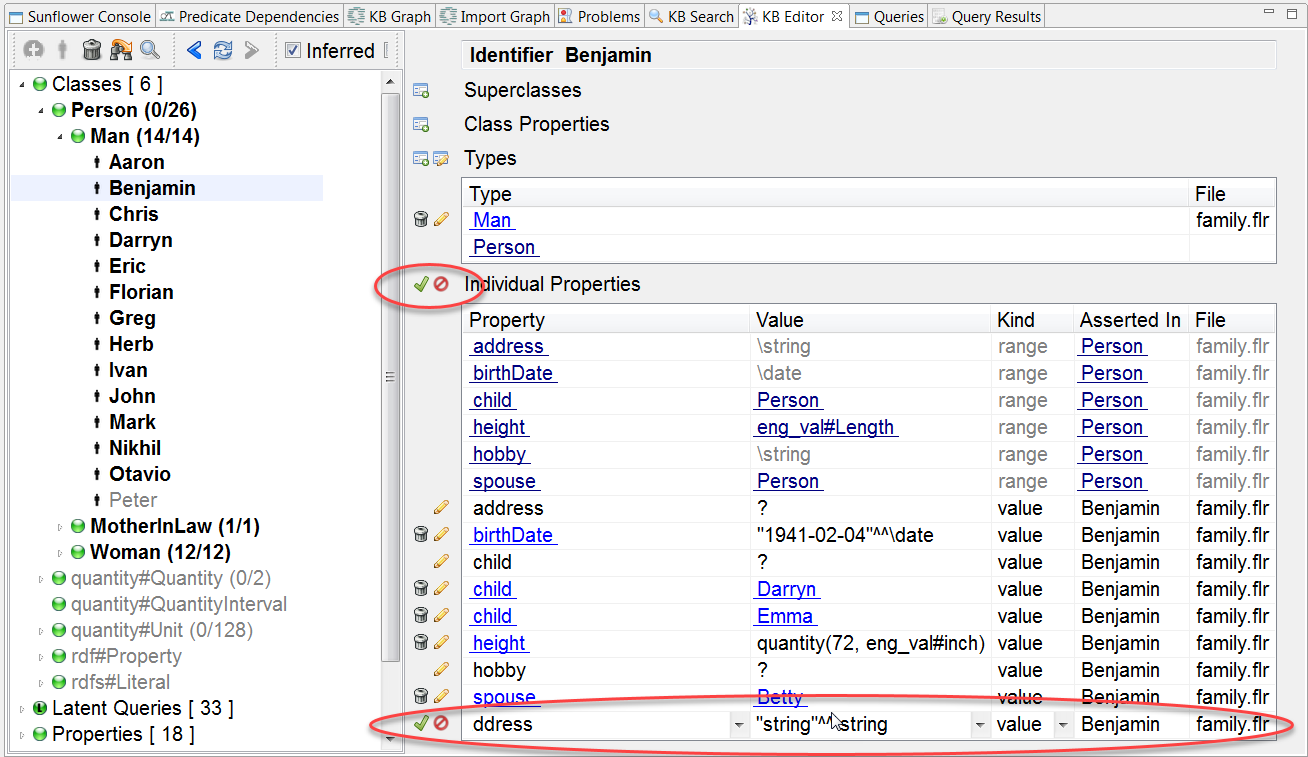
Fig. 172 New property row added to Benjamin’s property table
The pull-down menu of the Property field contains the default value of the new property, as well as Suggested Properties, Remaining Properties and New Property, as shown in Fig. 173.
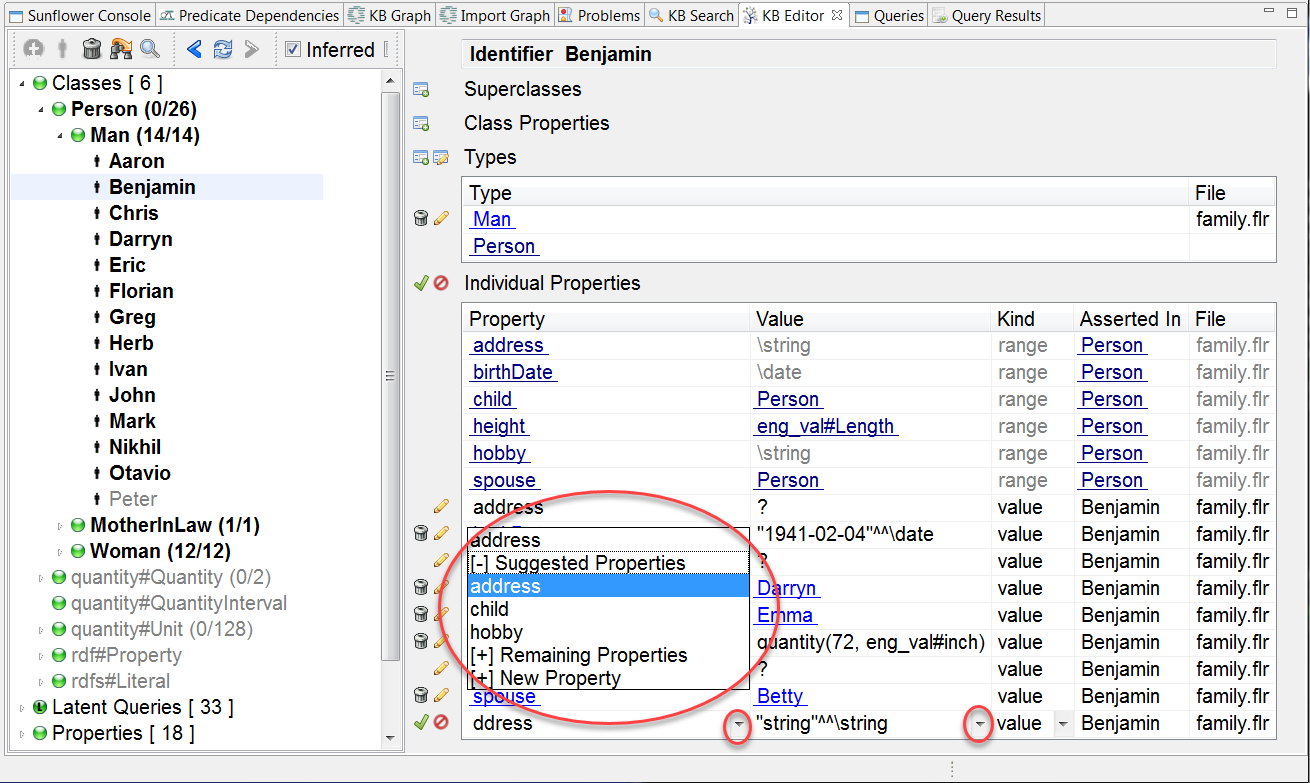
Fig. 173 New property pull-down menu
Suggested Properties are local or inherited properties which are not yet assigned any value, or can take on more assigned values according to the cardinality constraints.
Remaining Properties are all other properties excluding those which cannot take on more assigned values according to their cardinality constraints.
The default value is often one of the Suggested Properties. But it can also be one of the Remaining Properties if there is no Suggested Property which is unassigned or can take on more values. The default value is chosen so that the property can be assigned a value to satisfy its minimum cardinality constraint. For example, when a new property is added to individual Benjamin, the default value is address because this property hasn’t been assigned a value yet and it needs to be assigned to satisfy the minimum cardinality requirement of 1, as shown in Fig. 174.
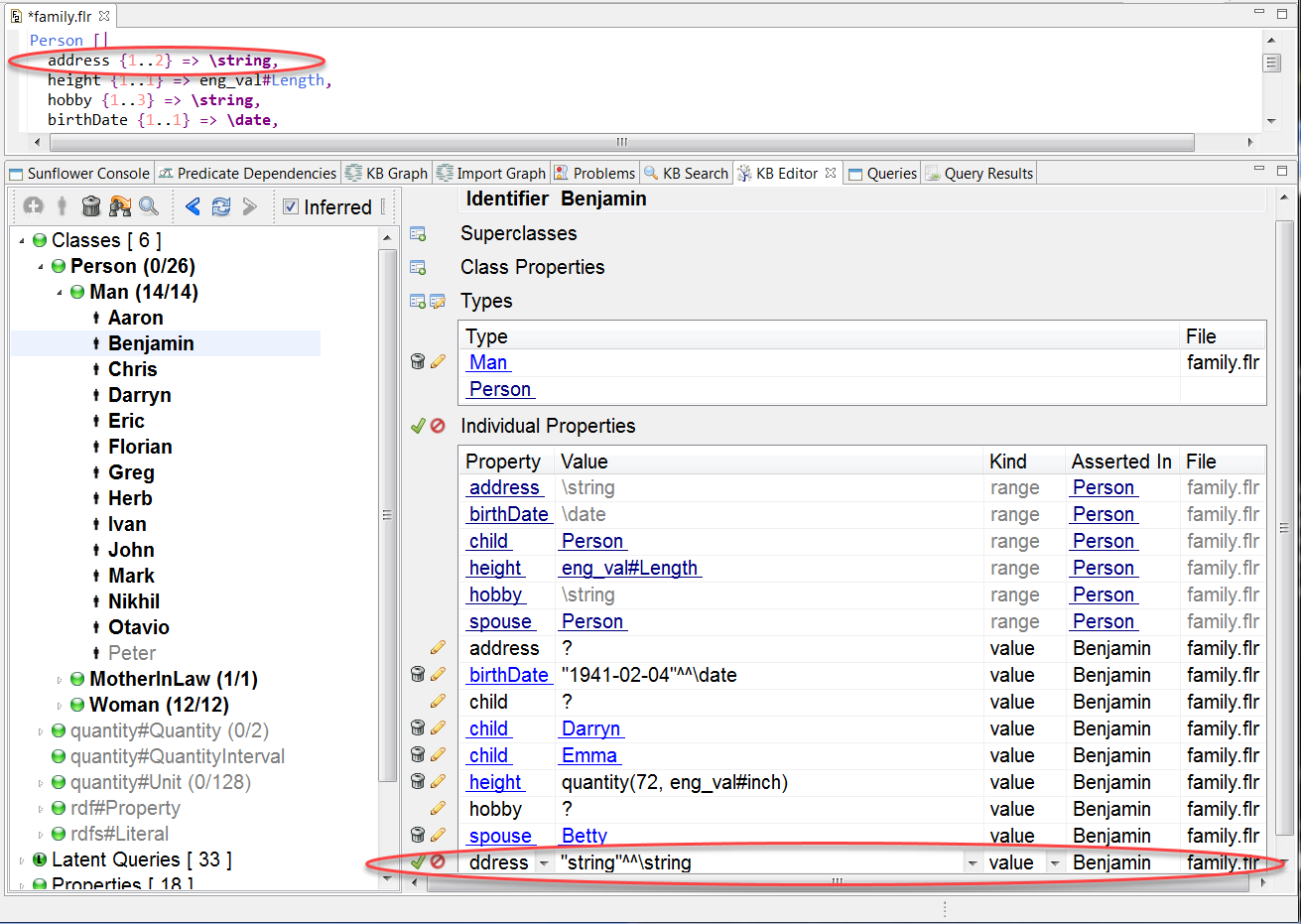
Fig. 174 New property has default value address
Edit the Value field of property address and type in “123 Main Street”. Click the green check mark to save it.
Add another new property for Benjamin. This time the default value shows hobby. That is because the property hobby has not been assigned any value to satisfy its minimum cardinality requirement of 1, as shown in Fig. 175.
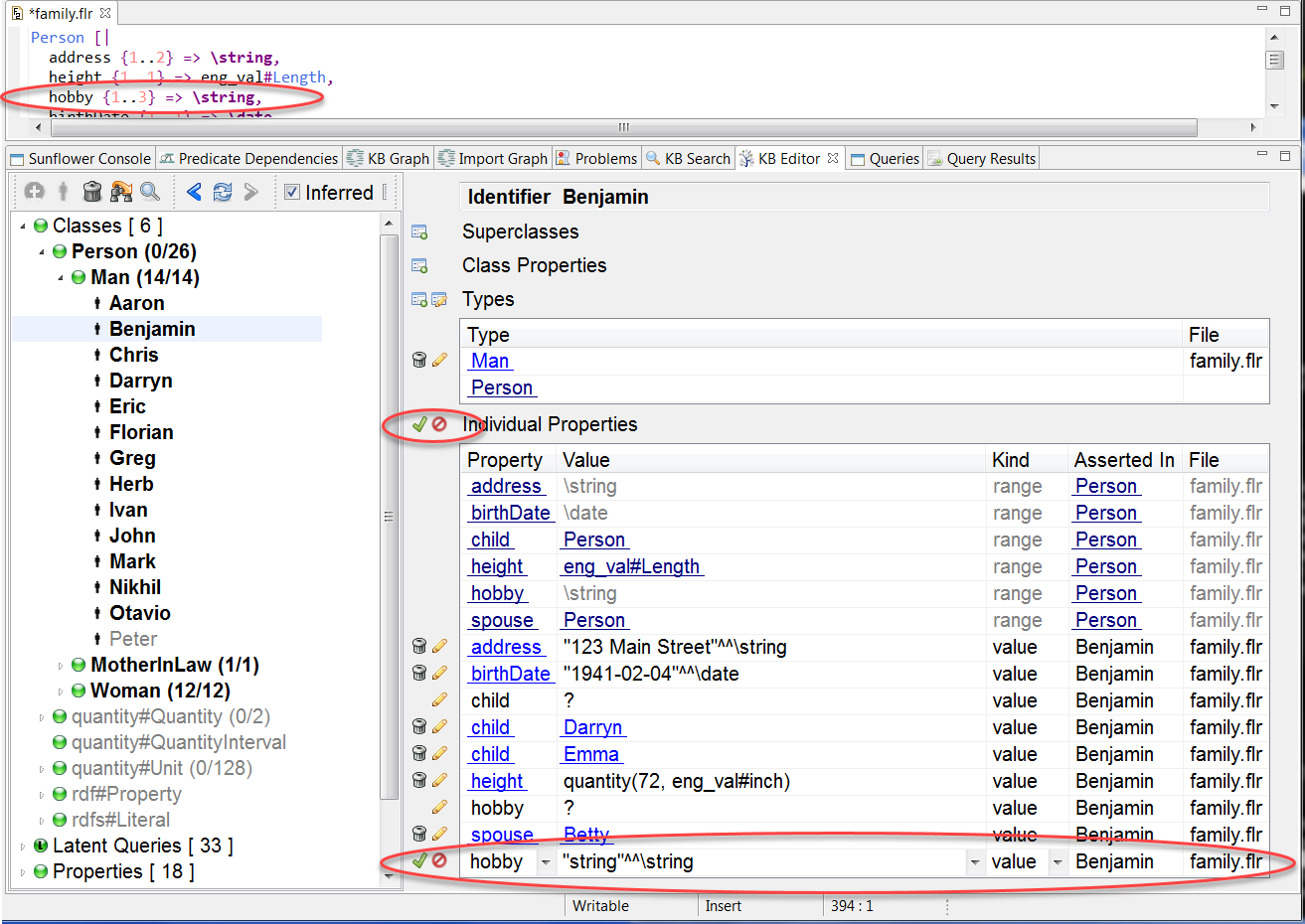
Fig. 175 New property has default value hobby
Edit the Value field of property hobby and type in “reading” and save this new property.
Once all properties have satisfied their minimum cardinality requirements, then a property which can take on more assigned values is chosen as the default. When two or more properties can take on more assigned values, the one with the biggest difference between its minimum cardinality and already assigned values is chosen as the default. For example, after assigning one address and one hobby to Benjamin, if another new property is to be added to Benjamin, the default value will be hobby. This is because hobby has a bigger difference between its minimum cardinality and already assigned values than the property address, as shown in Fig. 176. When there is a tie in the difference, the default is chosen at random.
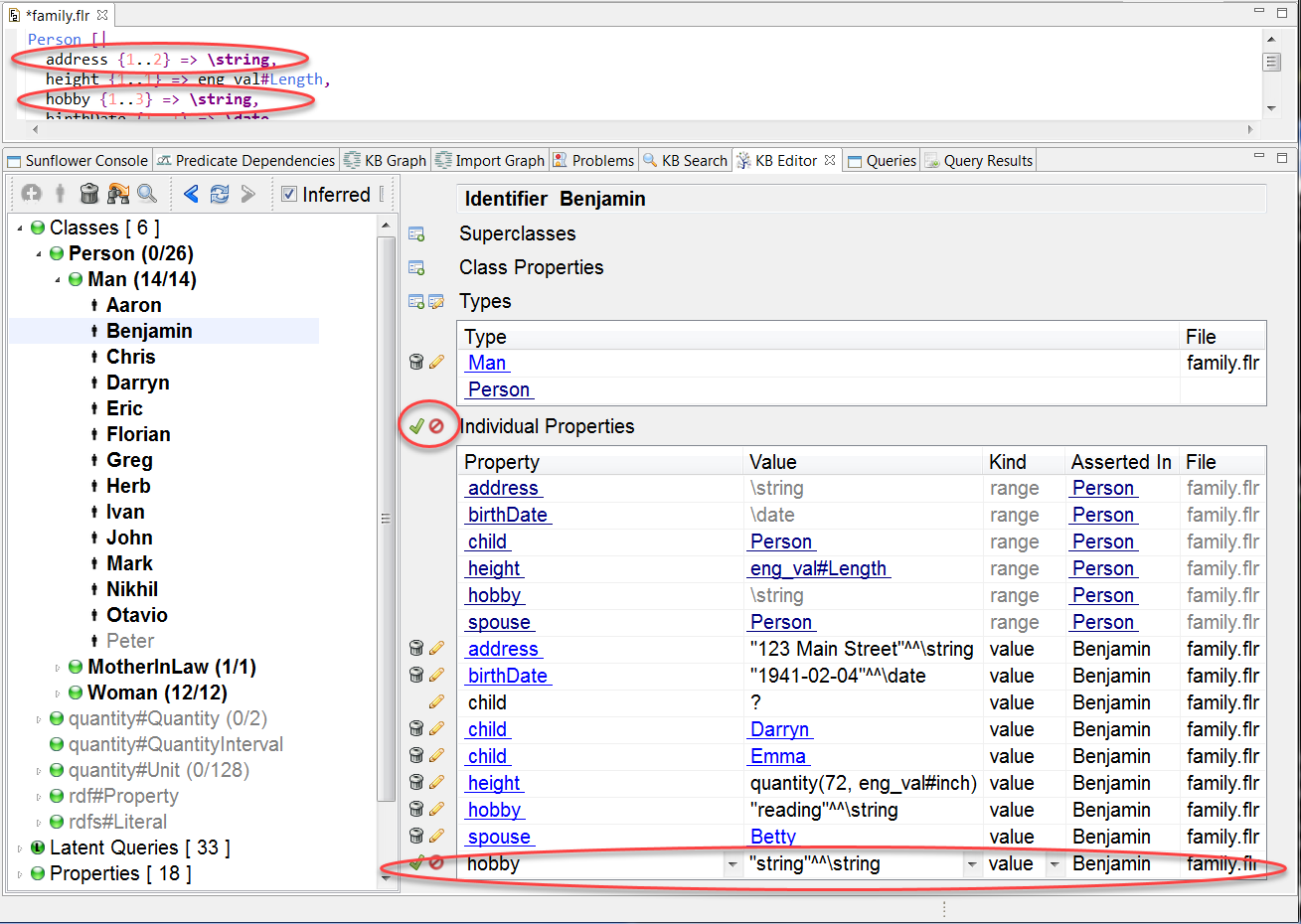
Fig. 176 New property has default value hobby because of its bigger difference between minimum cardinality and already assigned values